Revolutionizing molecular intelligence with CavitOmiX
The CavitOmiX copilot is an innovative tool specifically designed to predict side effects of drugs while addressing the challenges in this field with a unique approach.
Traditionally, it was believed that drugs bind to similar proteins, and thus, the landscape of similar proteins was screened to predict potential side effects. However, this approach fails to predict off-target sites in proteins structurally and sequentially unrelated to the intended drug targets.
With our proprietary technology, we focus on finding similar binding sites and deliberately neglect the overall structure and sequence similarity of proteins. Our AI-powered platform enables us to predict unexpected side effects caused by drugs binding to proteins with entirely different sequences and structures.
Screening 42k+ human proteins and their binding sites
The base of CavitOmiX is a meticulously constructed and curated dataset containing the proteins found in the human proteome, including splicing variants. This dataset was created by integrating state-of-the-art modeling tools such as AlphaFoldTM, OpenFold, and ESMFoldTM, which are part of the BioNeMo platform from NVIDIATM.
To ensure high quality and comparability of the dataset, we also employed homology modeling using our own proprietary CavitOmiX platform. Thorough post-processing by adding ligands and editing non-confident areas of the AI-generated models further enhances the datasets usability and value.
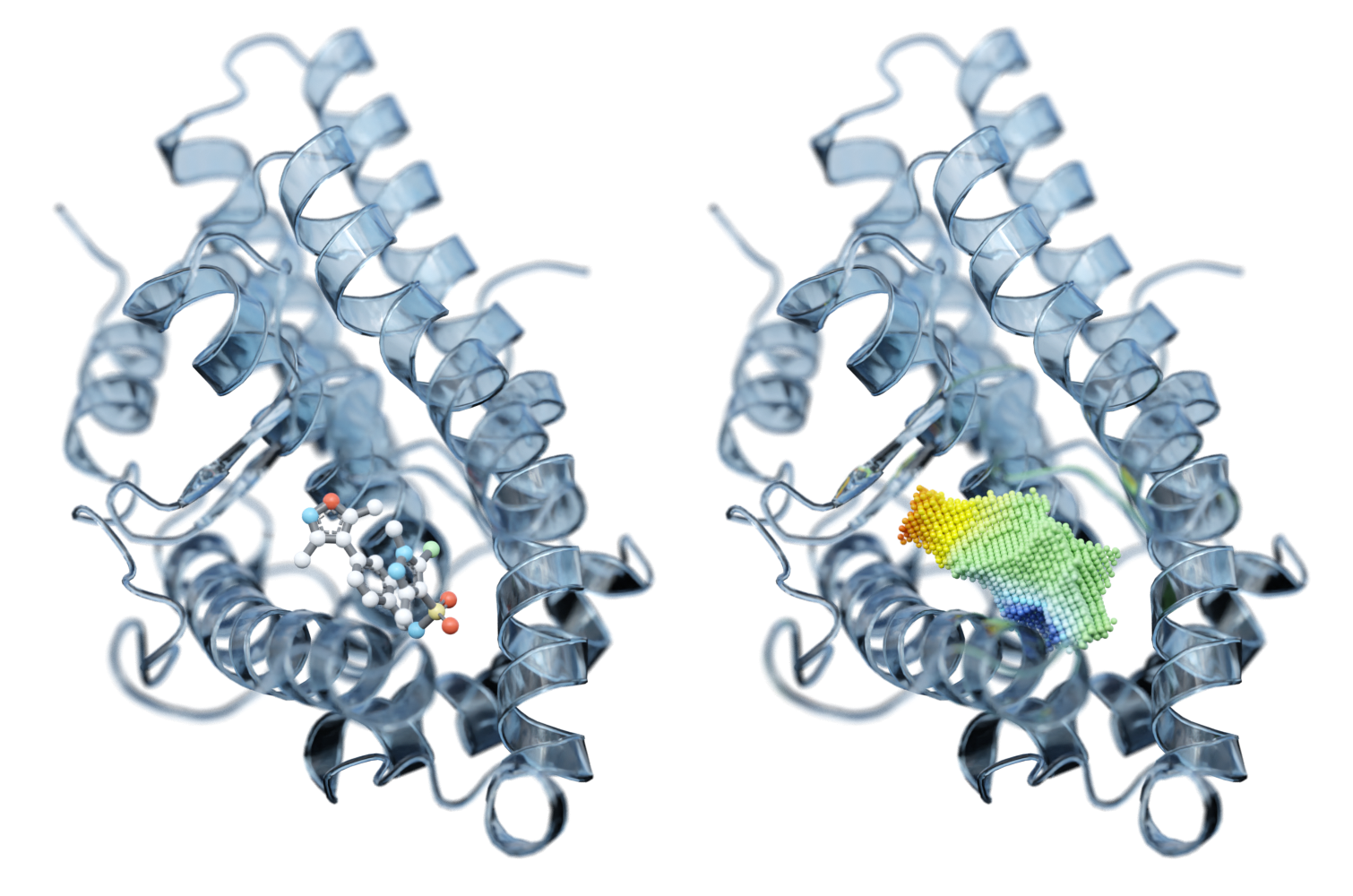
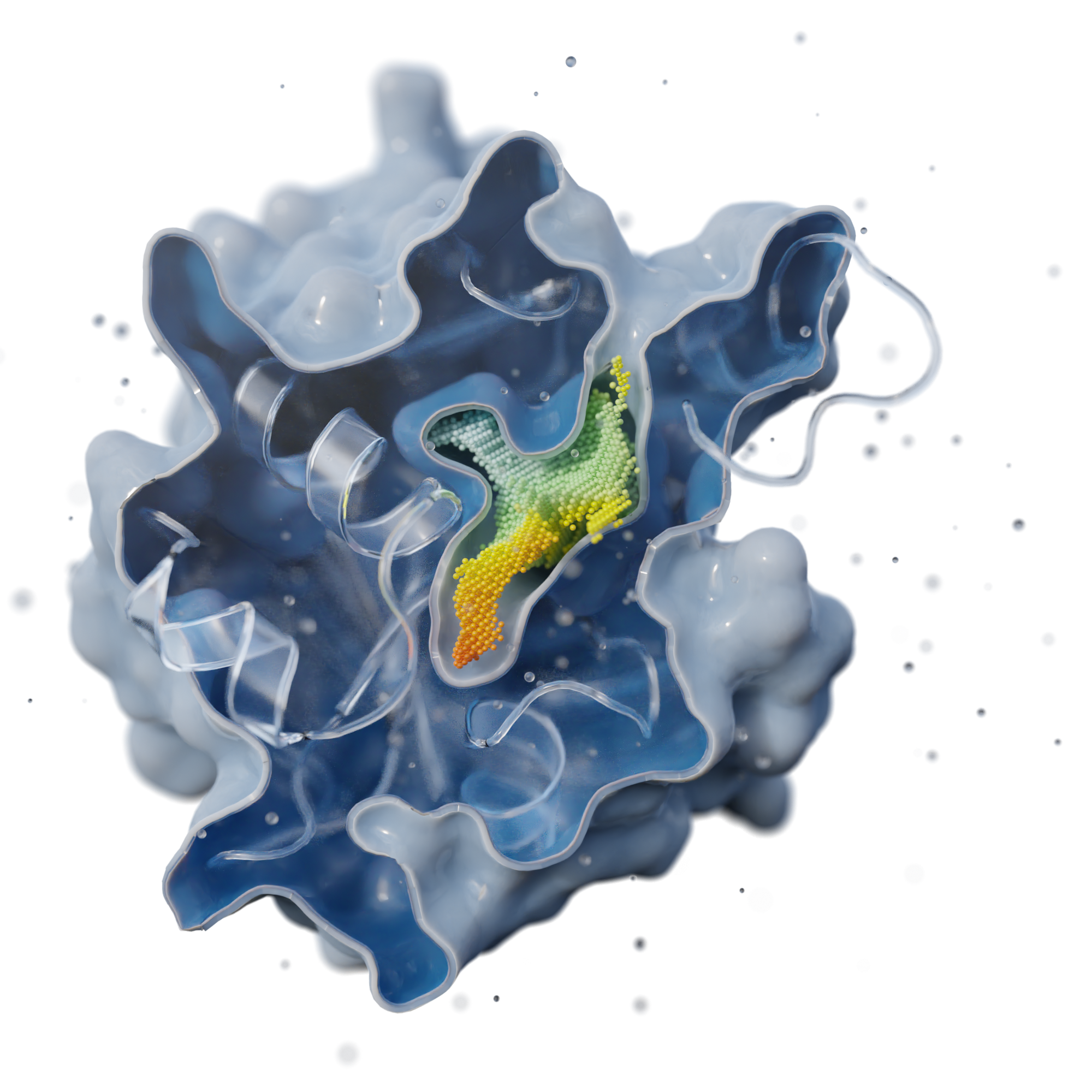
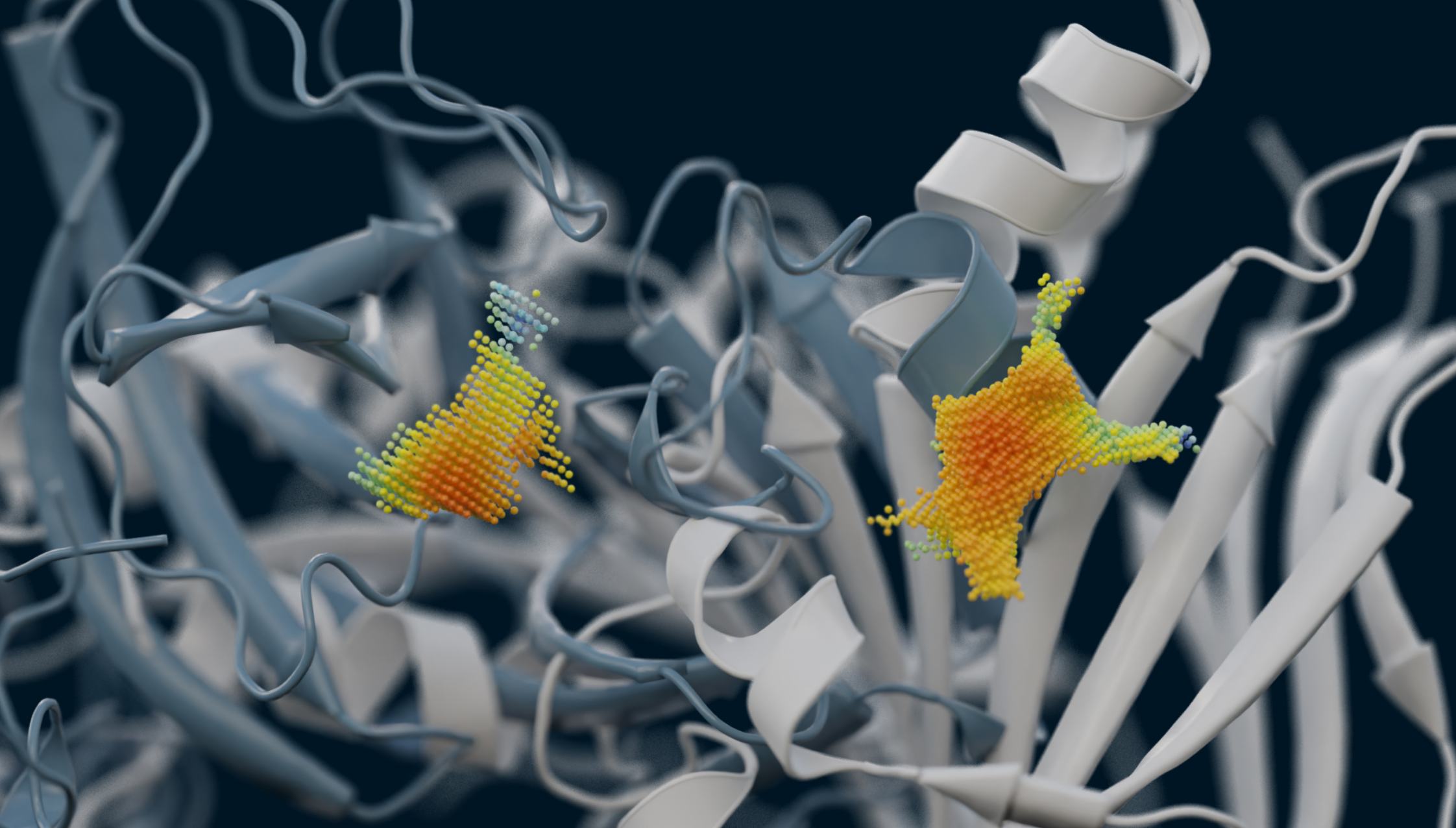
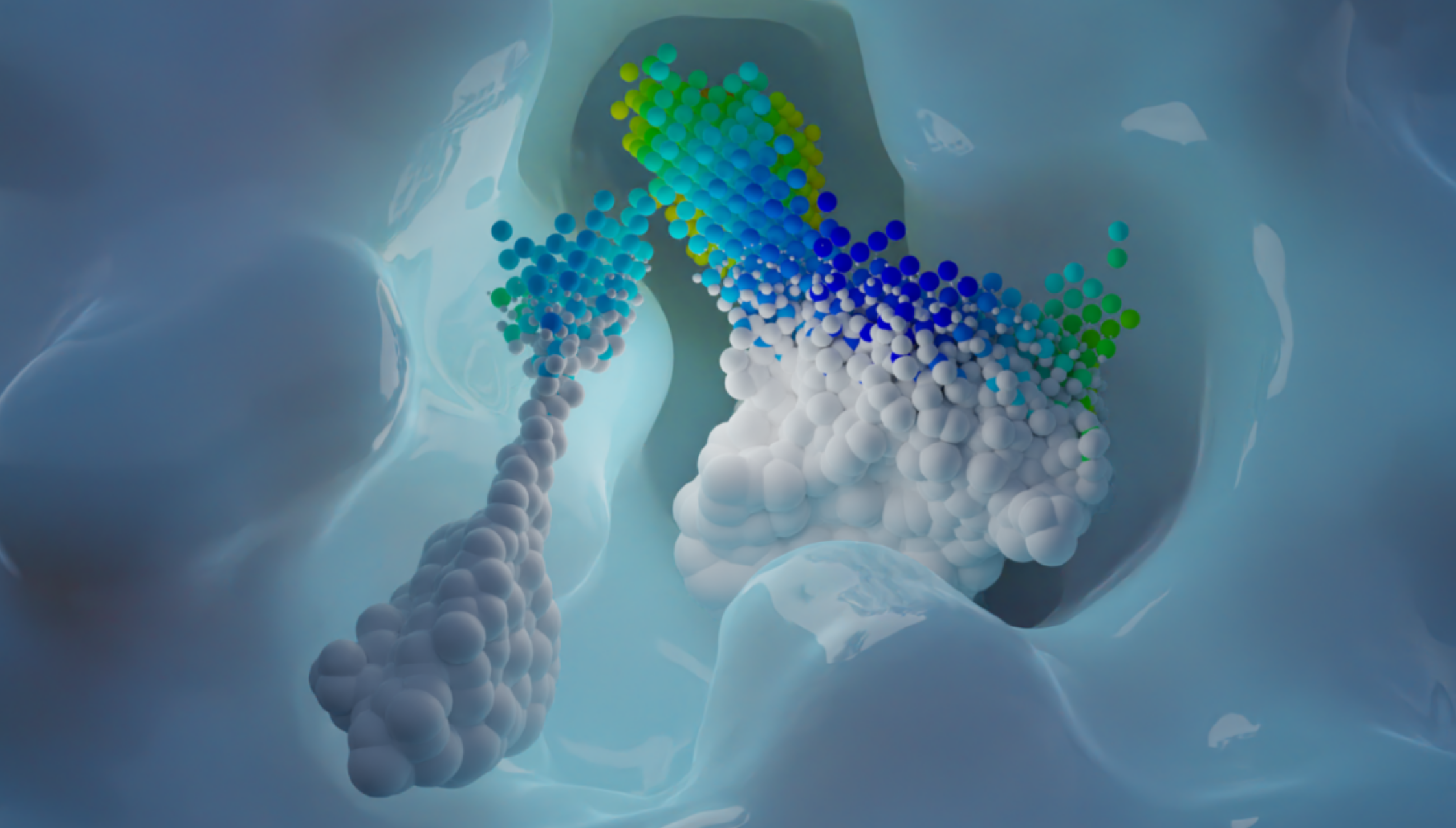
AI-powered algorithms & point cloud technology
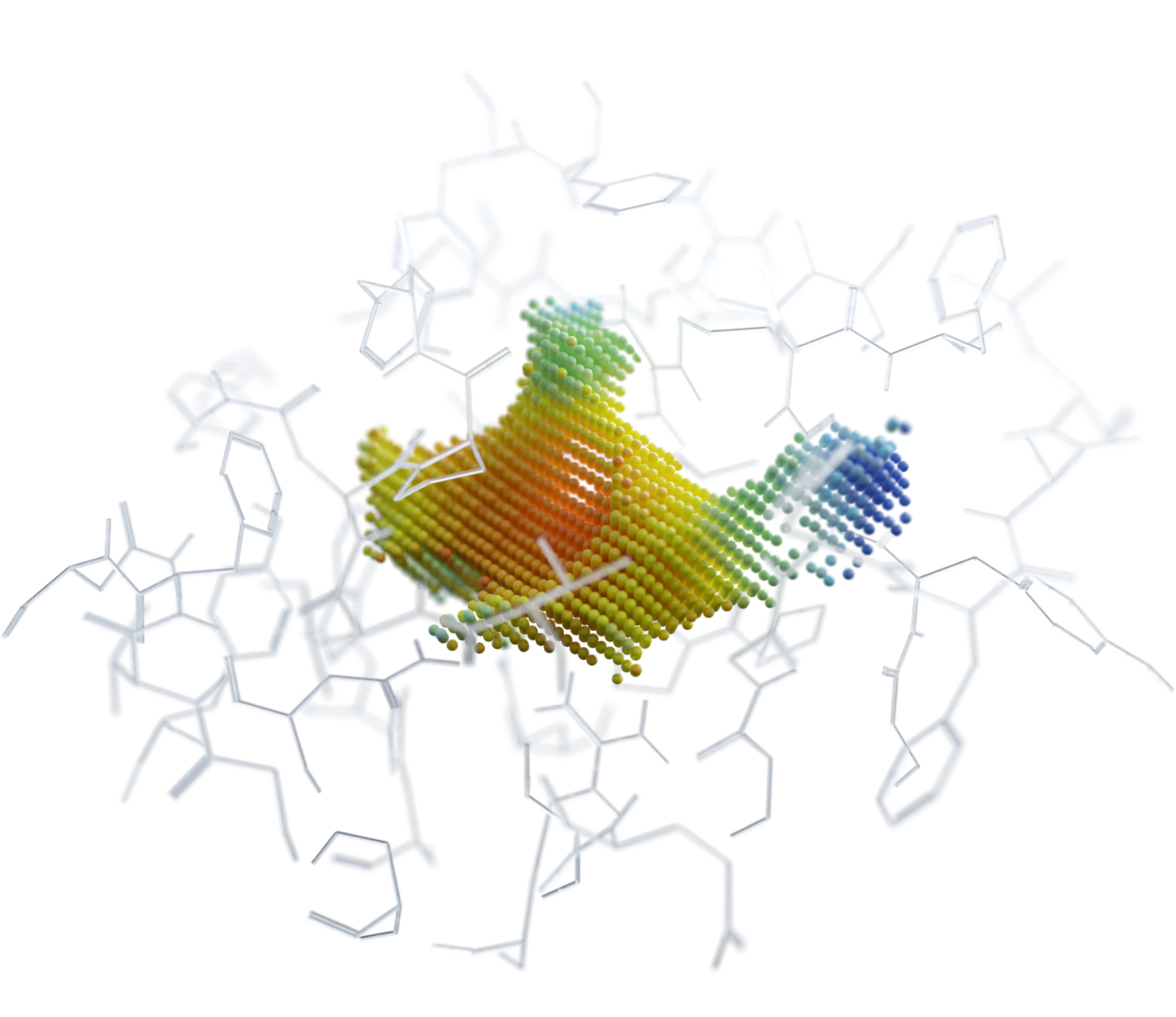
We analyze binding sites through point clouds, enabling us to precisely map various physico-chemical properties such as electrostatics, hydrophobicity, accessibility, hydrogen-binding potential, elasticity, and many more.
Our AI powered matching algorithm compares each point cloud in the human proteome with all the others, creating an interaction map. This map enables us to identify potential new drug binding sites, which may indicate off-target effects or suggest drug repurposing opportunities.
Our publications
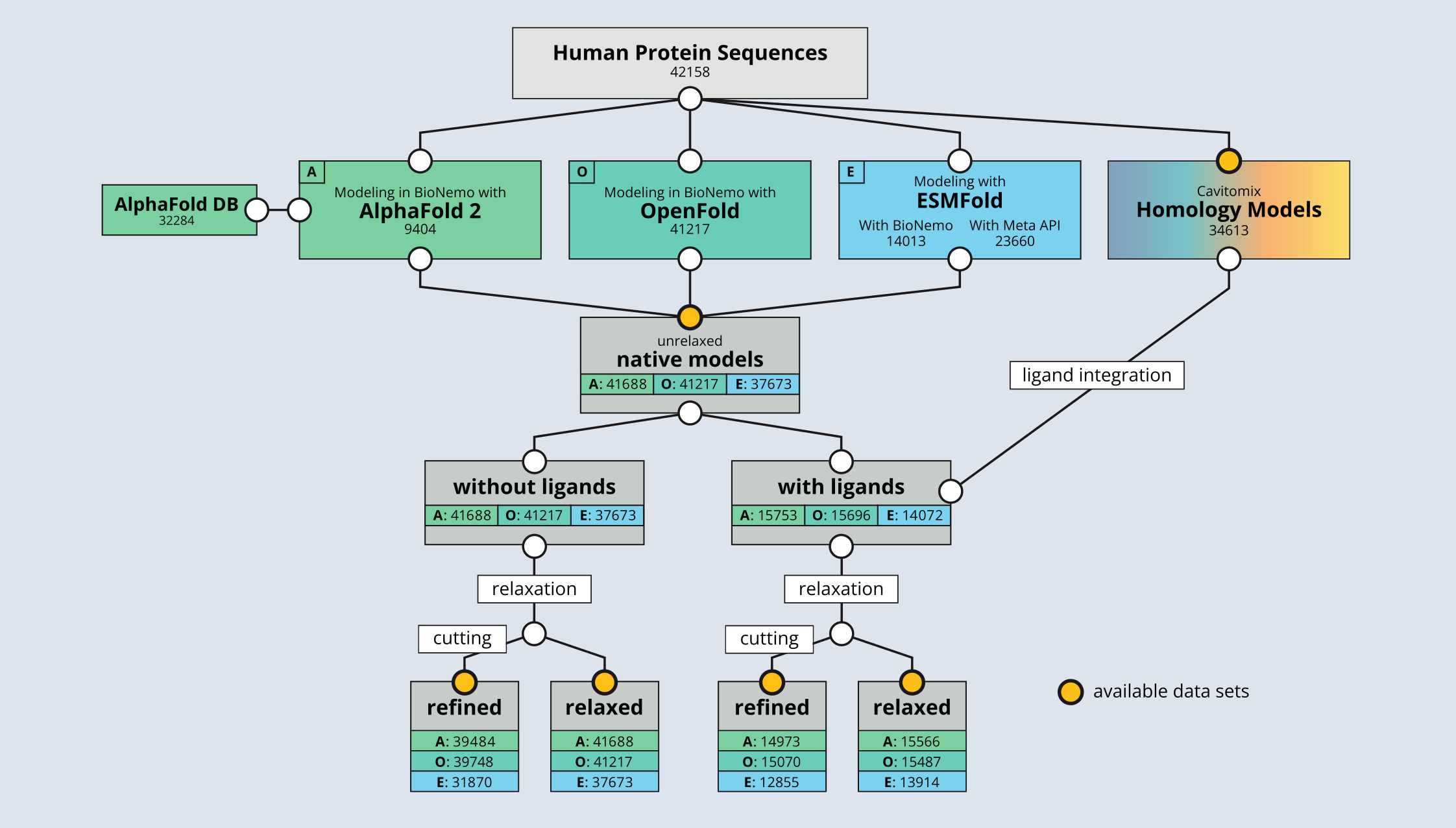
Folding the human proteome using BioNeMo: A fused dataset of structural models for machine learning purposes
Hetmann, M., Parigger, L., Sirelkhatim, H. et al. Sci Data 11, 591 (2024).
www.nature.com
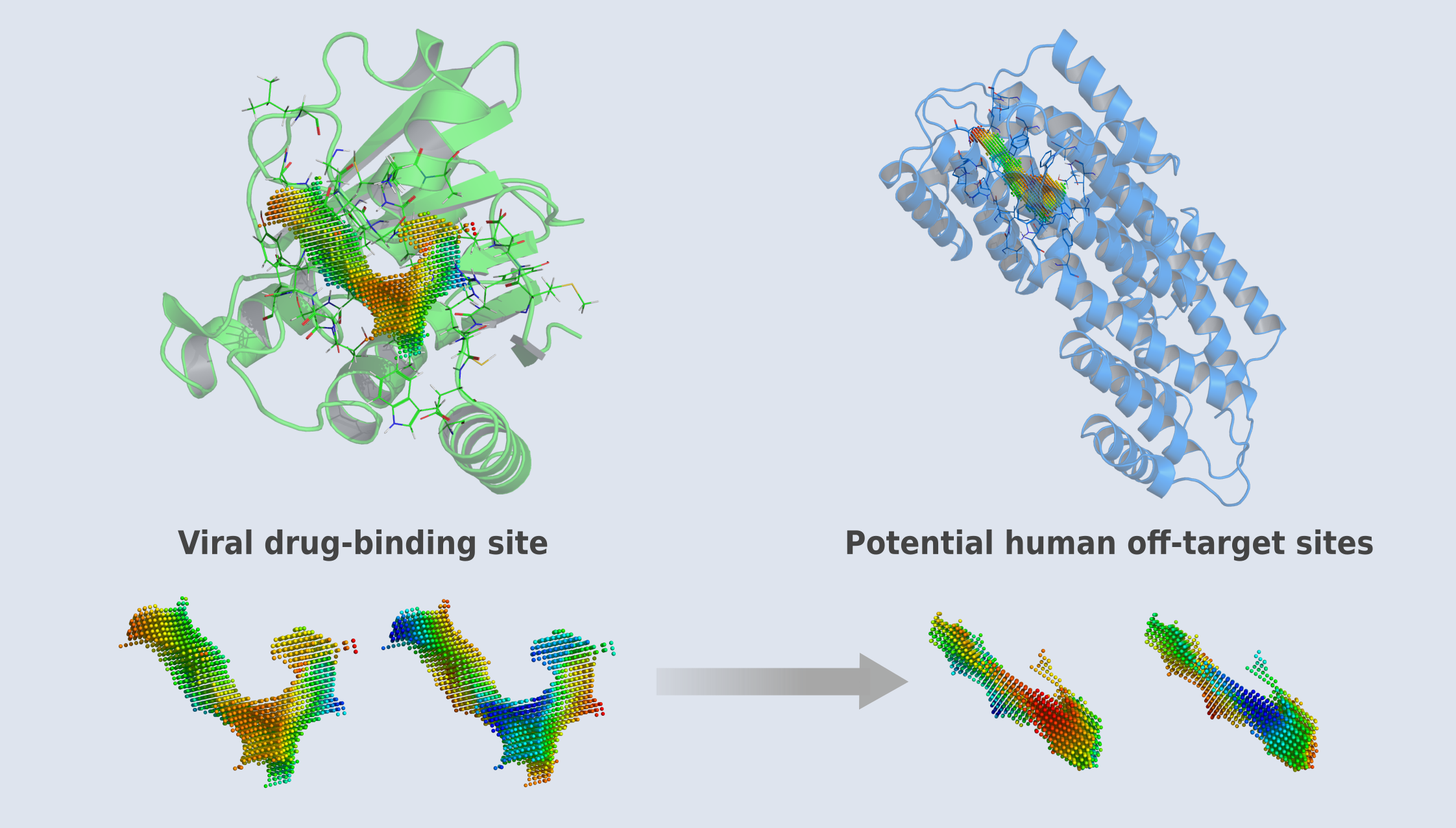
CavitOmiX Drug Discovery: Engineering Antivirals with Enhanced Spectrum and Reduced Side Effects for Arboviral Diseases
Parigger, L., Krassnigg, A., Hetmann, M. et al. Viruses 16, 1186 (2024).
www.mdpi.com
Identification and validation of fusidic acid and flufenamic acid as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 replication using DrugSolver CavitOmiX
Hetmann, M., Langner, C., Durmaz, V. et al. Sci Rep 13, 11783 (2023).
www.nature.com
Identification of promiscuous ene-reductase activity by mining structural databases using active site constellations
Steinkellner, G., Gruber, C., Pavkov-Keller, T. et al. Nat Commun 5, 4150 (2014).
www.nature.com